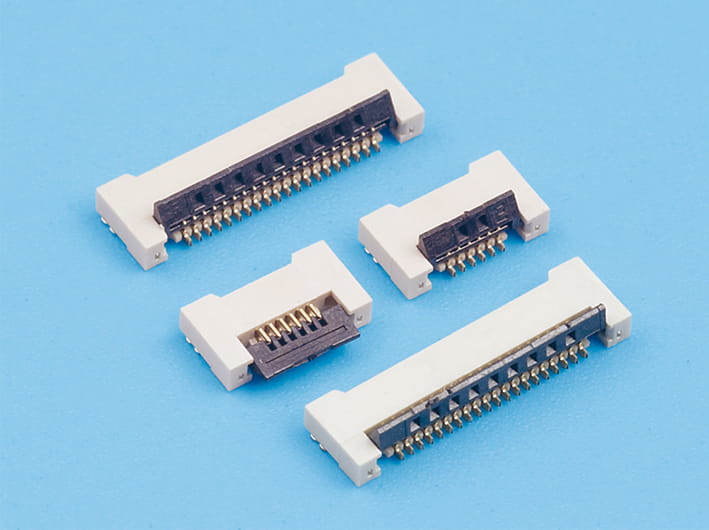
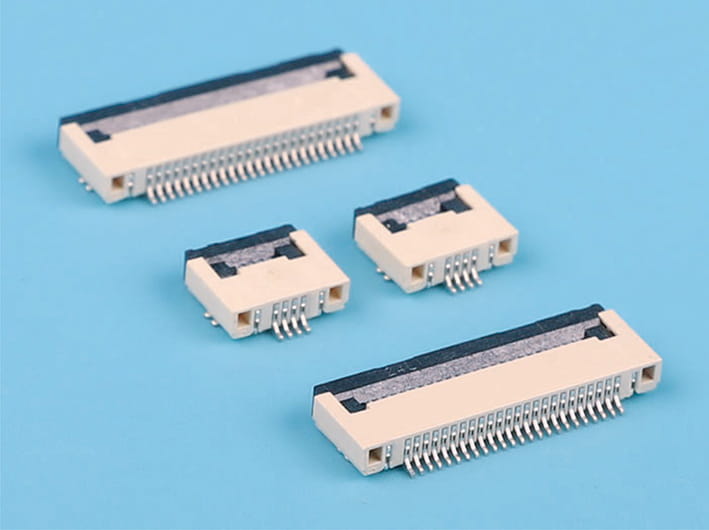
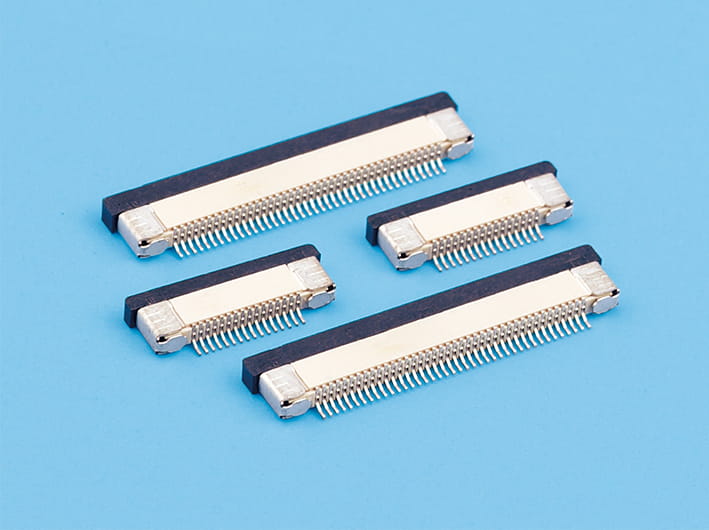
Heat Resistant Crimp Connectors for High-Temperature Industrial Systems
In industries that require durable and reliable electrical connections, heat-resistant crimp connectors are indispensable. These connectors play a crucial role in systems where high temperatures can cause traditional connectors to degrade, potentially cause system failure. Automotive crimp terminals, automotive wire crimp connectors, and heat-resistant crimp connectors have become essential components in high-temperature industrial applications, ensuring both performance and safety in harsh conditions.
The Need for Heat-Resistant Crimp Connectors
Industrial environments, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors, are characterized by the frequent use of high-power equipment, engines, and electrical systems that operate under conditions. In these settings, temperatures can rise significantly, and standard crimp connectors may not withstand such stresses over time. This is where heat-resistant crimp connectors come into play.
These specialized connectors are designed to operate effectively in high-temperature environments, maintaining electrical conductivity and mechanical integrity despite the challenges posed by heat, vibrations, and fluctuating temperatures. Whether in a high-performance automotive engine or an industrial furnace, the need for connectors that can endure heat is paramount. Automotive crimp terminals and automotive wire crimp connectors are commonly found in such systems, ensuring secure and stable connections that prevent performance issues or safety hazards.
Applications of Heat-Resistant Crimp Connectors
One of significant uses of heat-resistant crimp connectors is in the automotive industry. In automotive systems, especially in engine compartments and exhaust systems, components can be exposed to temperatures that regularly exceed 100°C (212°F). The high heat in these areas can degrade electrical connections, cause potential system malfunctions. Automotive crimp terminals and automotive wire crimp connectors provide the necessary protection, ensuring that wire connections remain intact and functional, even in these conditions.
Heat-resistant crimp connectors are also used extensively in manufacturing and heavy industry. In factories with high-temperature machinery, such as steel mills or chemical plants, these connectors help ensure the safe operation of control systems, sensors, and power distribution networks. Industrial systems in these environments often have to work under constant temperature fluctuations, which can stress components. Using crimp connectors that can tolerate such variations without failure is essential for the long-reliability and safety of these systems.
Why Choose Heat-Resistant Crimp Connectors?
There are several reasons why heat-resistant crimp connectors are becoming the go-to solution for high-temperature applications. First and foremost, they provide outstanding insulation and protection against high thermal stresses. The materials used in these connectors—such as high-temperature-resistant plastics, metals, and coatings—ensure that they won't degrade or become brittle under prolonged heat exposure.
Furthermore, automotive crimp terminals and automotive wire crimp connectors are engineered to offer enhanced electrical performance even at elevated temperatures. As temperatures rise, the resistance in a connector can increase, which can result in power losses, heat buildup, or even failure. Heat-resistant connectors are designed to reduce these risks, ensuring that electrical currents flow smoothly without unwanted resistance or degradation.
Durability is another critical advantage. In applications like automotive systems, automotive wire crimp connectors are frequently exposed to vibrations, moisture, and chemicals in addition to heat. The robustness of heat-resistant crimp connectors ensures that they can withstand these additional environmental factors without compromising performance.
Materials and Technology Behind Heat-Resistant Crimp Connectors
To function effectively in high-temperature environments, heat-resistant crimp connectors are made from materials specifically designed to resist thermal stress. Common materials include high-grade copper alloys for electrical conductors, combined with high-temperature-resistant insulating materials like silicone, Teflon, or fiberglass. These materials prevent connectors from melting or losing their insulation properties under heat.
In addition, advanced crimping technology plays a significant role in ensuring that automotive wire crimp connectors maintain secure connections. The crimping process itself must be precisely controlled to ensure a solid mechanical connection between the wire and the terminal, while also ensuring that the crimp does not damage the wire's insulation or conductor. This process is particularly important in high-temperature environments, where connectors are more likely to experience physical stress.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى